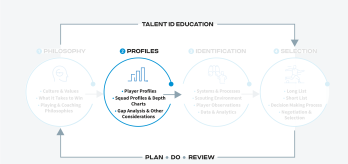
Talent identification is crucial for creating a successful football program. It lays the foundational groundwork that supports key areas like talent development, ultimately empowering them to achieve excellence. Building off Module 1 and 2 in the talent identification guide, an organisation, informed by its philosophy and profiles, should have a clear understanding of how it wants to play (i.e., philosophy) and the playing qualities of desired players (i.e., profiles). This third module highlights how to identify players with potential through well-structured systems and processes. It covers the use of comprehensive scouting environments, player observations, and data analytics to ensure effective and efficient identification of talent for the football organisation.
Why is this dimension important?
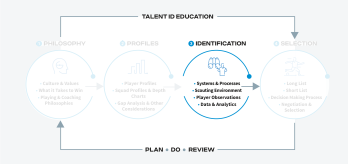
Identification involves determining the methods and processes required to identify players with the potential to perform at the highest level for a football organisation. Identification refers to the comprehensive systems and processes needed to scout and evaluate players, regardless of their location or competition level.
The identification dimension provides a structured framework for discovering talent. This framework encompasses systems and processes, scouting environments, player observations (e.g., reporting, live observation, video scouting), and data analytics, enabling informed decisions in player identification to build successful squads. Following the creation of a bespoke philosophy and profiles, organisations can effectively structure their talent identification process, aligning with their overall strategy.
To establish a comprehensive identification process, football organisations must implement robust scouting systems with appropriate resources and technical expertise to identify players across all levels and relevant locations. Investing in data management systems, talent identification events, player observation tools, and a network of specialists ensures comprehensive coverage of all relevant regions, maximising the talent pool.
How do you achieve success?
Implement talent identification systems and processes
The focus of implementing talent identification systems and processes is to determine a structured and effective method for scouting and reporting on players. A well-defined system ensures consistency, clarity, and efficiency in the talent identification process.
-
Who is responsible for designing the identification processes?
-
What scouting and reporting process (e.g., templates, linked to philosophy) do you currently use?
-
Does the organisation use a calendar or scheduling tool to effectively plan and coordinate talent identification activities and events?
-
Does the organisation use a range of structured and practical approaches to identify potential talent?
-
Do the scouts use common language and alignment?
-
Ensure reporting process and education is aligned to the philosophy and profiles.
-
Highlight how the scouting and reporting process can be conducted through a range of practical approaches, such as match observations, player recommendations, meetings, and conversations.
-
Consider the ages in which you begin identifying potential talent. Remember, the younger you start to identify players, the further away you are from the end goal (i.e., adulthood) and the less likely you are to be accurate in your decision making, therefore consider identifying players no younger than U12-U15.
-
The FIFA Football Language: Within this article you can better understand how FIFA analyse football through standardised language to break down each area in-detail in a way audiences world-wide can interpret.
Consider the scouting environment
The focus of considering the scouting environment is to establish a comprehensive and inclusive approach to identifying potential players. By understanding and optimising where and how scouting occurs, the organisation ensures that no talent goes unnoticed, and the recruitment process is efficient, effective, and capable of tapping into a diverse range of talent sources.
-
Where does the organisation identify their players (e.g., clubs, regional best with best sessions, schools)?
-
How does the organisation assess its football-playing population and the coverage of the playing environment (e.g., competition structures)?
-
Do you consider players based outside your borders/overseas?
-
Create a broad platform where players are identified from. For example, school football events, club games, competitions and tournaments, and player recommendations.
-
Consider collaboration with schools as well as other external stakeholders (e.g., grassroot programs) to support a greater environment.
-
Consider the impact of birthplace effects, recognising how certain locations may influence player development and opportunities.
-
Identify talent hotspots, regions that consistently produce a high volume of skilled players and leverage these areas for talent identification.
-
MODULE 3 | ACTIVITY PLANNING TABLE: This template refines intended talent ID activities, increasing alignment and accountability during strategic planning.
-
Australia seek stars of tomorrow as Talent Development Scheme is unveiled: Within this article you will find various examples of how Football Australia has enhanced and broadened their talent identification to different regions of the country, giving every talent a chance to be identified.
Conduct player observations
The focus of conducting player observations is to systematically assess and document the abilities and potential of players. Detailed and structured observations ensure that the talent identification process is thorough, standardised, and efficient.
-
Do you have player reports? If so, what level of detail do they include?
-
Do the player observations/scouting reports consider the relative age of each individual?
-
Do the player observations/scouting reports consider the maturation status of each individual?
-
What is the structure for organising player observation (e.g., how do you consider the experience/expertise of scouts in player observations or reports)?
-
Emphasise how player observations are crucial for identifying those with potential talent.
-
Highlight how the design of the player report that scouts and other possible stakeholders use when observing players is critical to align with philosophy and profiles as well as creating consistency.
-
Ensure that potential is being considered alongside performance when observing players.
-
MODULE 3 | CREATING PLAYER OBSERVATION TOOLS: In this resource readers can learn about the process and key principles adhered to when creating player observation templates.
-
MODULE 3 | LONG PLAYER OBSERVATION TOOL: This template can be used to create a thorough long-form report a player in the identification process.
-
MODULE 3 | SHORT PLAYER OBSERVATION TOOL: This template can be used to provide a more concise overview of a player in the identification process.
-
MODULE 3 | PERFORMANCE AND POTENTIAL MATRIX: With its two key dimension of performance and potential, this matrix helps you identify players that strike the balance of immediate impact and long-term value.
-
How scouts assess players: Within this research brief interview, you can hear about the insights from Dr. Tom Bergkamp and his research on how scouts in Netherlands observe and scout players.
-
Jan Verbeek on the relative age effect (RAE): In this science explained session, Jan Verbeek discusses the unfair advantages relative age effect presents for players and how this can be addressed.
-
Sean Cumming on maturation in youth football: In this science explained session, Prof. Sean Cumming describes maturation in football and its potential effects on performance and identification.
-
Oliver Höner on talent predictors: In this science explained session Prof. Oliver Höner discusses predicting potential in different facets of the game using technical and speed-related skills tests.
Implement data management
The focus of implementing data management is to establish a strong system for tracking, storing, and analysing player information. Effective data management facilitates informed decision-making and ensures that talent identification processes are objective, data-driven, and aligned with the organisation’s objectives.
-
What qualitative and quantitative data do you track? How do you track it?
-
What information storage do you use?
-
Do you have any talent pool tracking?
-
What tools do you use for visualisation and accessibility of talent identification?
-
Consider the type of objective data that is used to identify and track players.
-
Recognise the implementation of a data/performance analysis and/or insights department is essential to support data management.
-
Reflect on the collection and analysis of data through either, or both, internal and external data sources.
-
Emphasise the importance of information management and producing insights from various sources, including scouting reports, player biographies, and mapping exercises, to assess factors such as quality, style, regions, positions, and genders alongside statistical data.
-
MODULE 3 | QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE DATA COLLECTION METHODS: With this resource you can discover the main benefits of qualitative and quantitative data belonging to players in the identification process.
-
MODULE 3 | STORAGE AND VISUALISATION OF PLAYER DATA: This template outlines the importance of storing and visualising player data and provides a list of the types of information you should gather.
-
How Honduras' talent development system works: This presentation explores how Honduras’ use of observational data is helping coaches classify large numbers of players in a nationally aligned approach.
Reflection checklist
The following reflection checklist will enable a football organisation thoroughly examine and enhance key aspects of the identification process, ultimately facilitating player selections:
Summary
-
To ensure a productive talent identification process, sufficient time must be devoted to understanding and aligning identification efforts to the organisation’s philosophy and profiles.
-
Asking key questions highlighted in each subdimension will aid the development of comprehensive systems and processes, scouting environments, player observations, and data and analytics.
-
Considering the various important factors involved in each subdimension will ensure that identification efforts are efficient, streamlining the selection process.
-
Use the various good practice examples, tools, and additional resources embedded within this guide to ensure a more effective and efficient identification process.
















.variant64x64.png)
.variant348x164.png)