Talent identification is essential for building a successful football program. It establishes the foundation that underpins critical areas such as talent development, enabling them to reach their full potential and achieve excellence. Extending from Modules 1, 2, and 3, an organisation, shaped by its philosophy, profiles, and identification, should have a clear understanding of its culture and values, a defined set of key player qualities, and a structured framework for discovering talent. This fourth module outlines the procedures involved in the selection of players for teams. It addresses the creation and implementation of a long list, a short list, and the decision-making process to support player selection. This module also discusses the aspects of negotiation and selection as part of the final stages of talent identification.
Why is this dimension important?
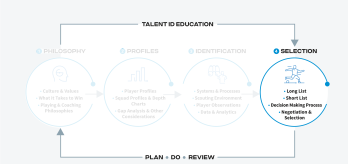
Selection is the critical phase where identified players are chosen for teams within a football organisation. This phase not only involves the final stages of player evaluation, but also includes the crucial steps of negotiation and formal selection of players into teams.
The selection dimension outlines step-by-step processes, including aspects of selecting players for teams within a football organisation. This involves creating long and short lists, establishing a decision-making process, and defining negotiation and selection procedures. It builds on the previous identification process, where potential players are identified in line with player and squad profiles as well as the organisation's philosophy.
To establish an effective selection process, football organisations must first create extended lists of players meeting basic playing requirements, followed by refined lists developed through detailed evaluations. A comprehensive decision-making process should also be put in place, clearly outlining the key stakeholders involved and their roles. Additionally, defining selection procedures, including any relevant negotiation processes and strategies, is essential for supporting a more effective and efficient selection process.
How do you achieve success?
Create long lists
The focus of creating long lists is to ensure a structured and thoughtful approach to building an extended pool of potential players. By asking critical questions and considering essential factors, organisations can develop comprehensive lists that reflect their fundamental playing requirements and align with their unique context.
-
How do you currently create a long list for your pool of talent and who is responsible for leading this?
-
Do the identified players on your extended list meet your desired playing qualities?
-
Do you have balance of different positions (e.g., multiple individuals per position) in your long list?
-
Do key stakeholders involved in the identification and selection processes have access to the long list?
-
Consider your football organisation’s playing philosophy to develop an extended list of players who align with these criteria.
-
Remember that the number and depth of lists is dependent on the football organisation’s context.
-
Consider how many players per age category, when the long list is drawn up, and how is it reviewed.
-
MODULE 4 │ LONG LIST: This template helps categorise and organise a comprehensive pool of potential players.
-
Getting agreement between scouts: Within this research brief interview, Dr Dennis Lüdin explains the difficulty in getting agreement between scouts on player potential, as well as possible solutions to make selection criteria more reliable.
Create short lists
The focus of creating short lists is to refine the pool of potential players on the long lists by conducting a collaborative and thorough evaluation process. By leveraging the insights of a multidisciplinary team and aligning with the organisation’s specific context and needs, short lists ensure a sharper focus on the most promising talent. This step is essential for streamlining decision-making and preparing for targeted player selection.
-
How do you currently create a short list for your pool of talent and who is responsible for leading this?
-
Do key stakeholders involved in the identification and selection processes have access to the short list?
-
Do you have a multidisciplinary team to audit and further evaluate players from the long list to create a short list?
-
Work collaboratively with a multidisciplinary team to create a short list of players to select from based on the long list.
-
Remember, similarly to the long list, the number and depth of talent on the short list is dependent on the football organisation’s context.
-
Consider, similarly to the long list, how many players per age category and positions when the short list is drawn up, as well as how it is reviewed.
-
Reflect upon the possible biases when selecting players on short lists, such as the influence of relative age and maturation, and implement strategies to mitigate against these affects.
-
MODULE 4 | SHORT LIST: This template helps refine a pool of potential players identified in a long list (like the one linked above) through a collaborative and thorough evaluation process.
-
A longitudinal investigation into the relative age effect in an English professional club: In this research brief, Dr Adam Kelly presents a study exploring the effects that nuanced age differences can have on the younger players within a youth team.
-
Biological maturation selection biases across playing positions in youth football: Within this research brief interview, Dr Liam Sweeney explains biological maturation selection biases across playing positions and discusses potential solutions to minimise its effect in youth football to maximise selection processes.
Implement a decision-making process
The purpose of implementing a decision-making process is to establish a clear and collaborative framework for evaluating and finalising key recruitment decisions. By defining roles, responsibilities, and structures, such as a formal decision-making board, organisations ensure that input from relevant stakeholders is effectively integrated, and final approvals are streamlined and accountable.
-
Who inputs into the decision-making process?
-
How often are player review meetings held for selections?
-
Who has final sign off on selection decisions?
-
What are you selecting for (i.e., purpose of the team)?
-
Outline who is involved and responsible for the decision-making process.
-
Create formal meetings with an agreed decision-making board/group.
-
Consider multi-department collaboration to inform the decision-making process.
-
MODULE 4 | RACI MATRIX: Within this document, readers can find a template they can use in their working environment, along with an explanation of how to use it.
-
MODULE 4 | DECISION-MAKING PROCESS: This resource provides a logical framework outlining steps and guiding principles to support the player decision-making process.
-
Future Teams and Talent ID in Belgium: Within this video presentation, Belgian FA Sport Scientist Arne Jaspers explains how Belgium uses future teams to keep late-developers in their talent pool as they mature, and also discusses the use of technology to better inform decision-making processes for scouts and key stakeholders in talent identification.
-
How Denmark is addressing the relative growth effect: Within this video presentation, Danish FA’s Rasmus Hallander Porse explains how Denmark is countering relative growth effects using future teams where late developers, who are at different stages of their development, are given selection opportunities.
-
The Swiss FA’s Footuro and Footura development programmes: Within this video presentation, Swiss FA Director of Talent Development Patrick Bruggmann discusses the Footuro and Footura talent development program aimed to select and prioritise the development of individual players over short-term results and success.
Outline negotiation and selection procedures
The focus of outlining negotiation and selection procedures is to create a transparent, strategic, and collaborative framework for finalising player selections. By defining clear processes, identifying key stakeholders, and incorporating checks and reviews, organisations ensure that both the negotiation strategy and selection decisions align with strategic goals while continuously refining and improving the process to maximise approaches.
-
What is your negotiation process and strategy?
-
What is your selection procedure?
-
Who is responsible for checking and challenging selection decisions?
-
Who are the key stakeholders (internal and external) in the selection procedures (e.g., parents, agents)?
-
Consider your strategic approach when selecting players and consider the players personal circumstances.
-
Note how the external stakeholders (e.g., parents, agents) could play an important role.
-
Record, analyse, and review transparent discussions with designated persons during the selection decisions to improve procedures.
-
MODULE 4 | STAKEHOLDER MAPPING TOOL: This document consists of a template that can help you identify, evaluate, and prioritise stakeholders that influence or have an interest in a football organisation’s player selection process.
-
MODULE 4 | PLAYER NEGOTIATION PROCESS: This resource offers a step-by-step approach for a structured and effective player negotiation process within a competitive professional football club.
Reflection checklist
The following reflection checklist will help a football organisation critically assess and improve key aspects of the selection process, ultimately supporting the effective selection of players:
Summary
-
To ensure an effective selection process, football organisations must align their selection efforts with their identification approaches, profiles, and philosophy.
-
Asking key questions throughout the selection process, such as those related to long lists, short lists, decision-making, and negotiations, helps build comprehensive and effective systems for player selection.
-
Considering important factors, such as team balance, the involvement of relevant stakeholders, and establishing clear roles and responsibilities, ensures a streamlined and collaborative selection process.
-
Leverage good practice examples, tools, and resources provided within this guide to refine and continually improve the selection process for ongoing success.














.variant64x64.png)
.variant348x164.png)